The Vertical Spread Option Strategy is a trading strategy that can be used in several different situations. Most successful traders utilize some form of this strategy regularly to increase their profits and limit their risk.
In this article we are going to cover :
What Is A Vertical Spread?
The Different Types Of Vertical Spreads
What Are The Risks Of Using A Vertical Spread Strategy?
Why Use A Vertical Spread Strategy?
When To Use A Vertical Spread Strategy
How To Place A Vertical Spread Trade
Real quick guys. Please click the like and subscribe buttons right now which helps me to create more videos to get out and it will allow you to be notified when future videos are released.
Let’s start by defining a vertical spread.
What Is A Vertical Spread?
A vertical spread is a directional strategy made up of long and short puts/calls at different strikes in the same expiration. Vertical spreads allow us to trade directionally while clearly defining our maximum profit and maximum loss on entry (known as defined risk).
The Different Types Of Vertical Spreads
Long Call Vertical Spread
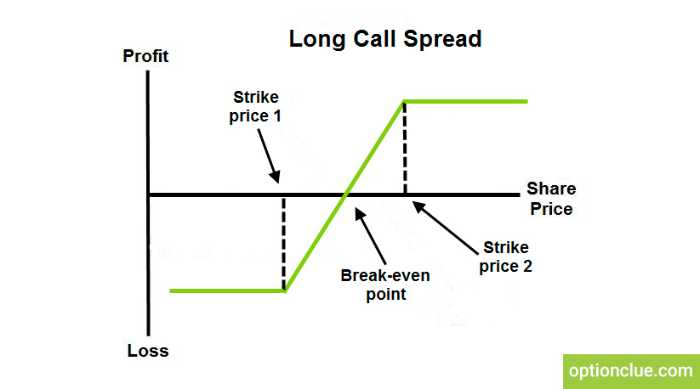
A long call vertical spread is a bullish, defined risk strategy made up of a long and short call at different strikes in the same expiration.
Directional Assumption: Bullish
Setup:
– Buy ITM Call
– Sell OTM Call
Ideal Implied Volatility Environment: Low
Max Profit: Distance Between Call Strikes – Net Debit Paid
How to Calculate Breakeven(s): Long Call Strike + Net Debit Paid
Long Put Vertical Spread
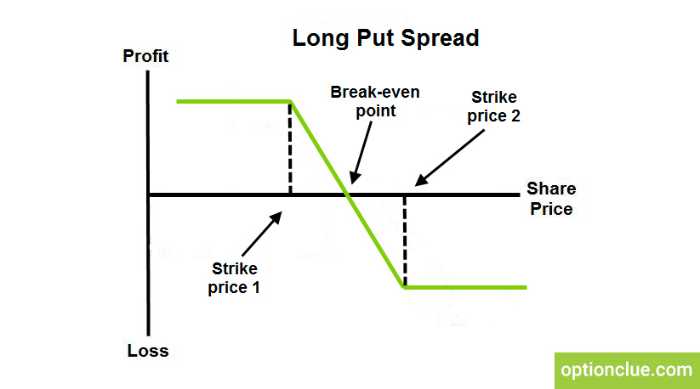
A long put vertical spread is a bearish, defined risk strategy made up of a long and short put at different strikes in the same expiration.
Directional Assumption: Bearish
Setup:
– Buy ITM Put
– Sell OTM Put
Ideal Implied Volatility Environment: Low
Max Profit: Distance Between Put Strikes – Net Debit Paid
How to Calculate Breakeven(s): Long Put Strike – Debit Paid
Short Call Vertical Spread
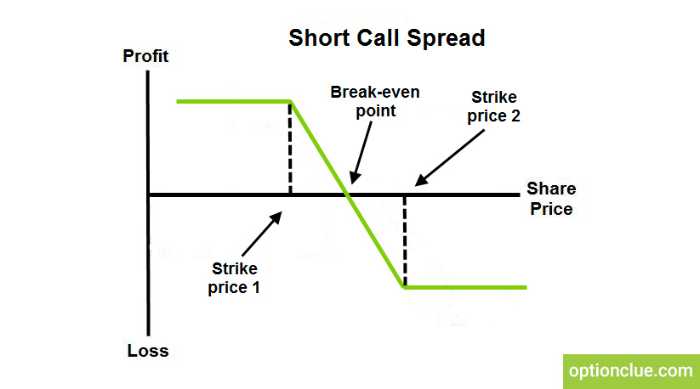
A short call vertical spread is a bearish, defined risk strategy made up of a long and short call at different strikes in the same expiration.
Directional Assumption: Bearish
Setup:
– Sell OTM Call (closer to ATM)
– Buy OTM Call (further away from ATM)
Ideal Implied Volatility Environment: High
Max Profit: Credit received from opening trade
How to Calculate Breakeven(s): Short call strike + credit received
Short Put Vertical Spread
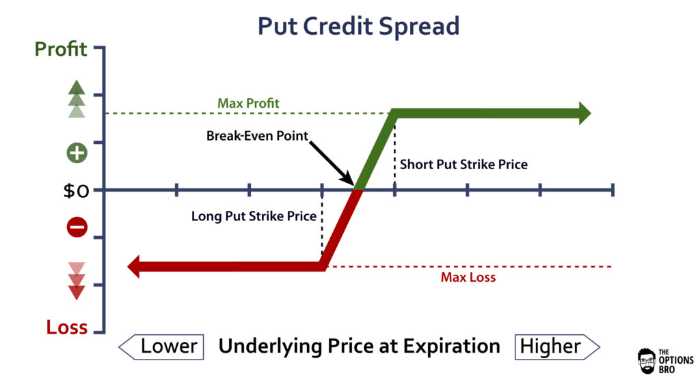
A short put vertical spread is a bullish, defined risk strategy made up of a long and short put at different strikes in the same expiration.
Directional Assumption: Bullish
Setup:
– Sell OTM Put (closer to ATM)
– Buy OTM Put (further away from ATM)
Ideal Implied Volatility Environment: High
Max Profit: Credit received from opening trade
How to Calculate Breakeven(s): Short Put Strike – Credit Received
Buying Versus Selling Vertical Spreads
Buying versus Selling, Short verus Long and Credit versus Debit. What??
When we “SELL” a Vertical Call Spreads we are “SHORT” a Vertical Call or Put Spread. By doing this, we “BUY” a Vertical Call or Put Spread we are “LONG” a Vertical Call or Put Spread.
When we Short or Sell then we receive a Credit. At the same time, when we Buy or go Long it costs so we need to pay for the spread. This will be a Debit.
We typically like to sell vertical spreads in high volatility since they will have a better POP or probability of profit. When we buy vertical spreads they are only a 50% POP or probability of profit so they are a lower probability trade. We typically only recommend doing this in low volatility and when we are very bullish or bearish.
What are The Benefits of Vertical Spreads?
There are a couple of key benefits of vertical spreads which is why they are such a popular strategy amongst options traders.
First of all, they are Defined-Risk trades. So one of the biggest advantages of vertical spreads is that your maximum risk is known from the outset. This is in contrast to many other option strategies which involve unlimited risk.
Vertical Spreads also have Limited Capital Requirements – This is because when you sell vertical spreads you are buying a protective put or call. This makes the trade defined risk so you are only required to put up the maximum loss amount for the trade. If you are buying the spread then your max outlay is when you put the trade on.
When is the Best Time to Use a Vertical Spread?

Vertical spreads allow us to trade directionally while clearly defining our maximum profit and maximum loss on entry (known as defined risk).
While implied volatility (IV) plays more of a role with naked options, it still does affect vertical spreads. We prefer to sell premium in high IV environments and buy premium in low IV environments.
We like to put on vertical spreads with about 45 DTE Days To Expiration.
When IV is high, we look to sell vertical spreads hoping for an IV contraction. When IV rank is low, we look to buy vertical spreads to stay engaged and also use it as a potential hedge against our short volatility risk.
How do we Manage Vertical Spreads?
Since the maximum loss is known at order entry, losing positions are often not defended.
Some people prefer to roll the spreads at about 21 days to expiration. We look to roll for a credit which is sometimes difficult with vertical spreads. If we cannot roll for a credit, we can let the trade expire for the loss and hope that the stock bounces back.
When do we Close Vertical Spreads?
Profitable vertical spreads will be closed at a more favorable price than the entry price. A good profit goal is around 50% of maximum profit.
How do we put on a Vertical Spread?
And we will show you using a real example on the TastyWorks Option Trading Platform.
Selling a Vertical Spread Example
To better understand how to sell a Short Put Vertical Spread, let’s look at an example.
We are going to sell a Short Put Vertical Spread in SNAP since it has a high IVR of 73 and we think it is a good stock at the lower end of its trading range. So we are bullish and expect it to go up in price. We will use the TastyWorks Trade platform. By the way I’ll put the link in the notes below if you want to open an account and get the free stock promotion. It is the option trade platform that I use most of the time and I think it’s the best for trading options.
So we are going to go to the trade tab and punch in the ticker SNAP up above. I like to use the curve mode so that I can visually see the profit zone in green.
We go to the strategy tab and select Short Put Vertical. The TastyWorks platform will automatically set you up to sell a short strangle.
In this case the stock is at 31.73. We are selling the 31 strike put and buying the 28 put. By doing this, we collect $122 immediately upon placing this trade. We place the trade with 32 Days To Expiration.
The BP effect which is buying power we are using is $178. So it is a cost-efficient way of investing since are using $178 and collecting $122.
Now if you look at the green area which is the P&L at expiration, we see the max profit is the $122 which is the amount we collected upfront. We like to collect 1/3 the width of the strikes on a vertical so we are doing it in this case. As long as the stock stays above the 31 put strike we keep the max profit.
We don’t start losing money until the stock moves to around $30. So if the stock stays where it is at or even moves down a little we are still profitable.
Conclusion
The Vertical Spreads are a great strategy to use when you are directional on a stock and want to limit your risk. You can collect high premiums and they don’t use a lot of buying power.
Always do your research and consider your investment goals before you begin trading stock options. For more stock and financial information, please check out our other resources at OptionsFinanceProfits.com.